Looking back to the ancient times, when our forbearers had a profound knowledge of the night clear skies, modern people get the notion of the great significance of the star constellations throughout the centuries in terms of navigation, spiritual life, mythology and even universal truths about the humble place of humans in this endless world.
Greek mythology has proved to be by far the most useful source for the star constellations, since Ptolemy was the first to identify 48 constellations back in the 2nd century. Babylonian, Egyptian, Roman mythologies and others should also be marked as noteworthy in the modern astronomical knowledge. In the course of time the particular mythological characters and stories may have undergone some alterations, however, the rough images and forms of the constellations have kept a relative similarity to the ancient ones.

Since 1922, The International Astronomical Union has made a list of 88 constellations, which are visible in the night sky all around the world. Even though there are clear star maps with the exact location of the constellations, you still need to take into account your exact location, the time of the year, the season, and even the artificial light pollution. The good vision of the constellation images could be enhanced by the usage of technical tools such as a telescope or binoculars. These devices help you enjoy the observation of fainter stars, or other astronomical and astrological features as nebulae and star clusters. No matter which constellation is the viewer’s main goal, the North Star is a universal point of orientation. Another interesting fact is that almost all of the star constellations are visible for half a year, although their best naked eye visibility lasts within a specific month of the year depending on the observer’s location either in the Southern or the Northern hemisphere.
In addition to the natural and technical features that could ease the opportunity of star constellation sightings, on line applications could be quite as handy. Starmap, Astroviewer or Google sky are some of the web tools that are of great assistance to all star constellation gazing adventurers.
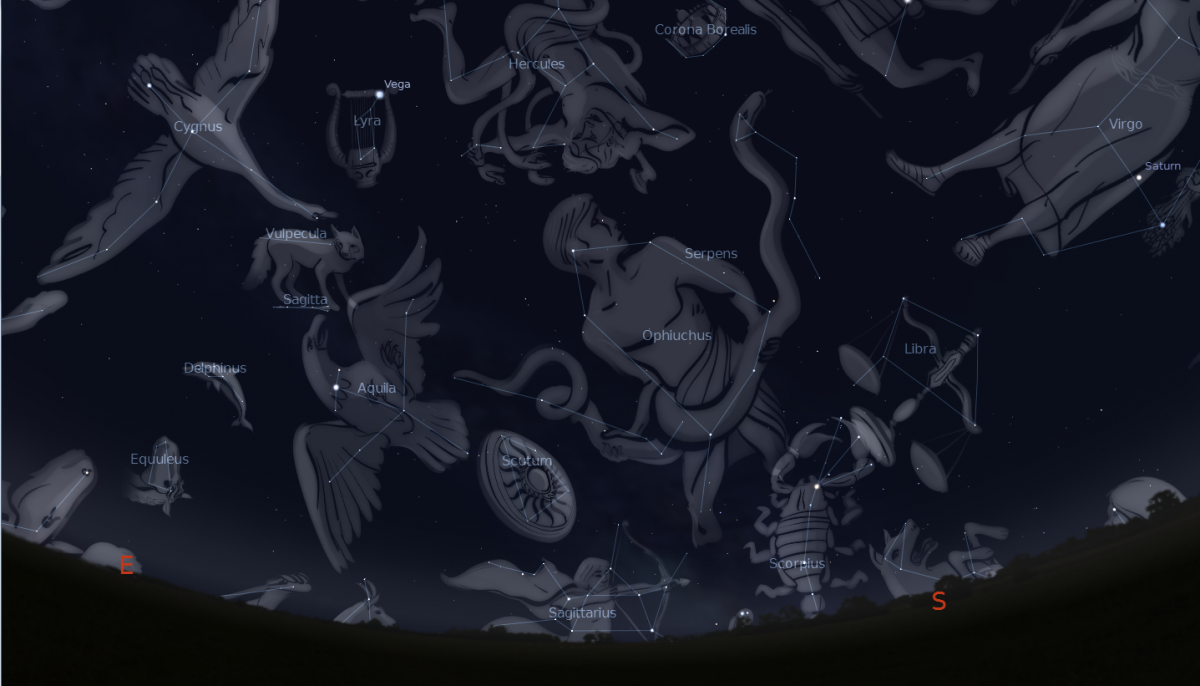

Here are some of the main facts concerning star constellations.
A clear cut definition of the term is a useful introduction to the topic. The simple definition of a constellation covers the idea of a group of stars, perceived together as a pattern in the night sky. Yet, one should not ignore the existence of an official definition of the term, which refers to a patch of the sky where all stars within the constraints of that area are part of the star constellation.
The Northern hemisphere, as well as the Southern hemisphere, have their own star constellations. This means that some star forms are only visible in the Northern hemisphere, and others are only visible in the Southern hemisphere.

In case there are constellations that could be seen in the two hemispheres, their sighting may seem upside down if viewed in the southern hemisphere.
Most star constellations are seasonal(they could only be seen in winter or only in summer) and occupy the night sky in specific period of the year. Yet, there are some stellar patterns that can be observed throughout the whole year. An example of an all-year-long constellation is Ursa Major, which can be viewed in the Northern hemisphere.
The earth’s constant rotation causes the movable position of the stars in the sky. Consequently, the image of the sky at a particular time at night will be quite different from what you would see several hours before or after that particular time.
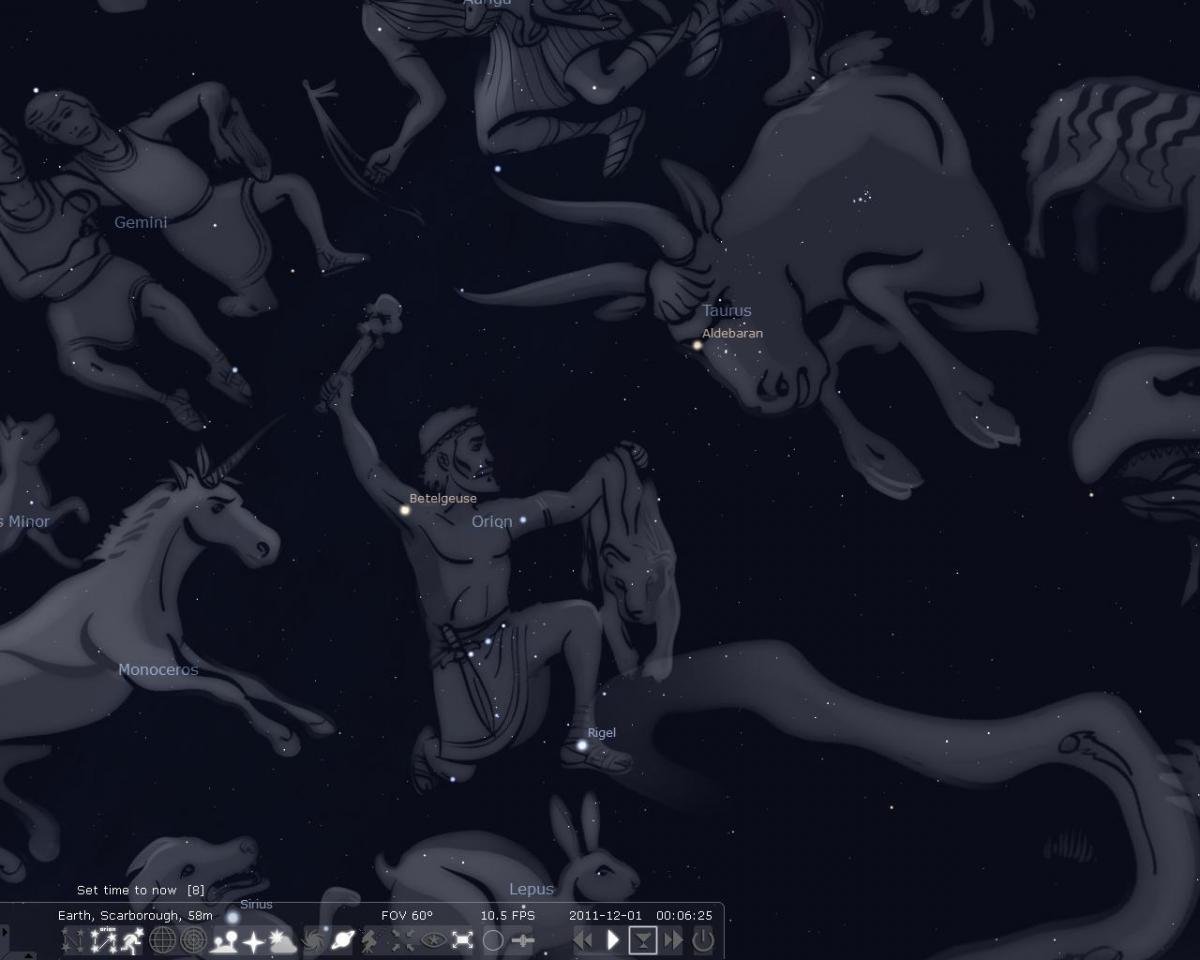
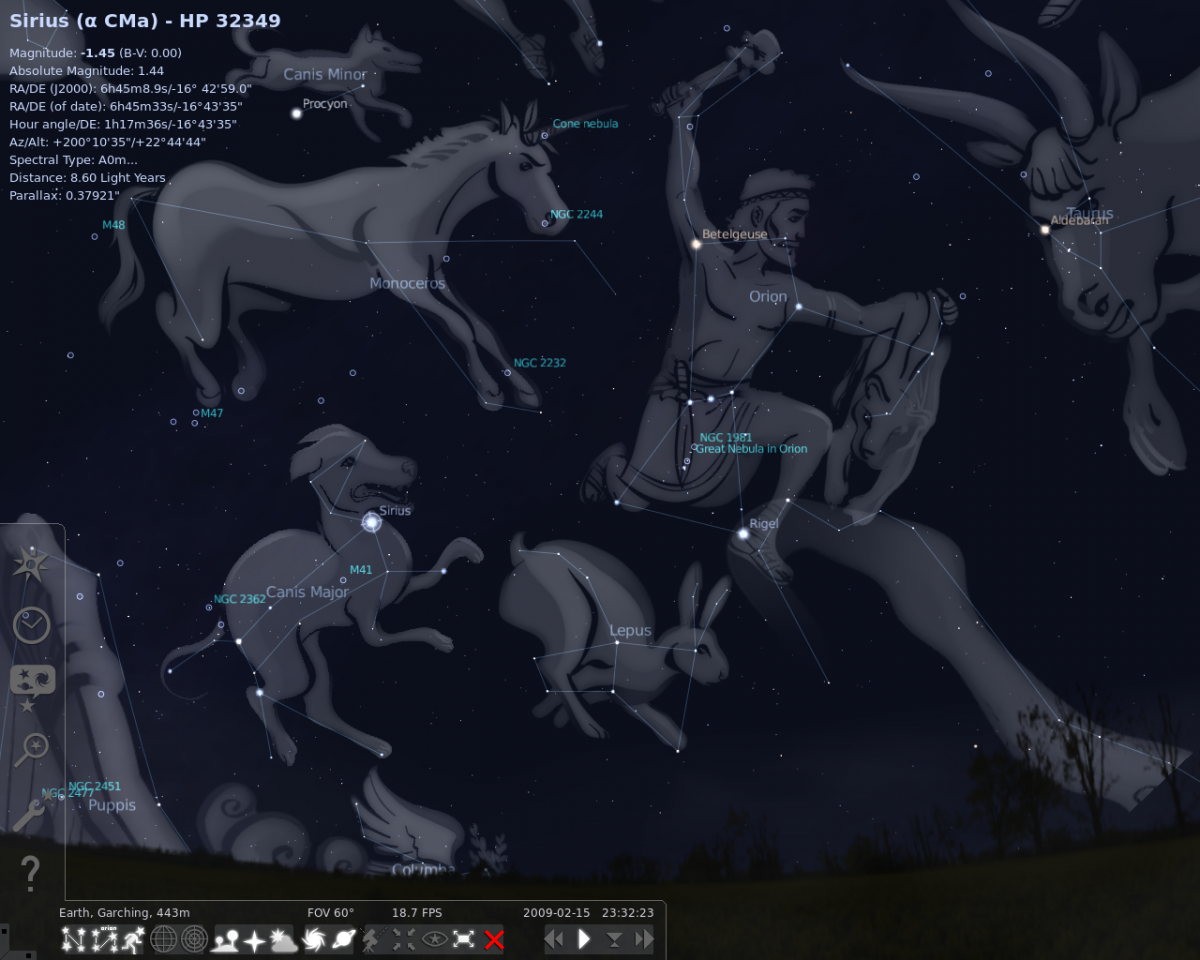
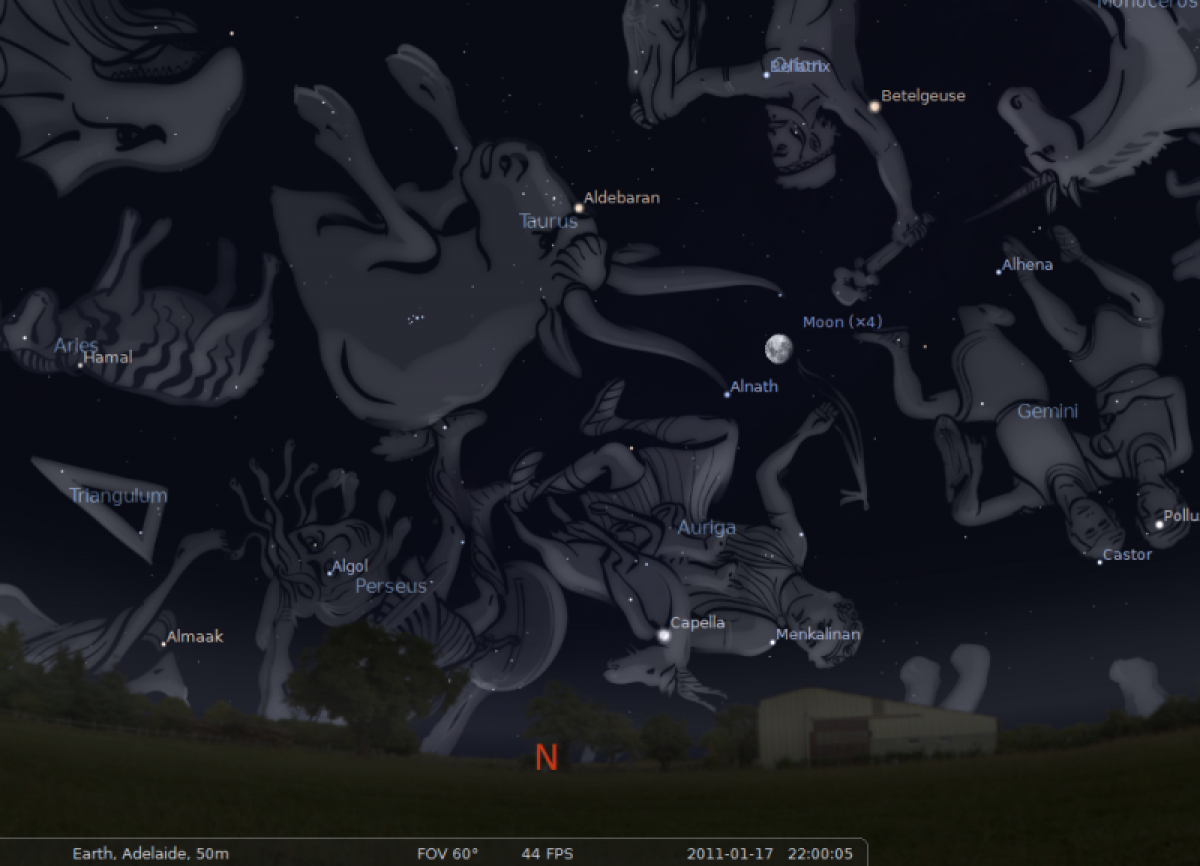
Star constellations also consist of remote galaxies and nebulae
The Big Dipper is the most prominent instance of an asterism, which is also worth defining. Asterisms are star formations which are part of one or multiple star constellations. Thus, the Big Dipper is a group of stars that forms a pattern
within the star constellation of Ursa Major.
The galaxy of the Milky way knows only one star that is not part of any constellation, and this star is our sun.


Leave a Reply